Protein is crucial in bodybuilding, serving as the fundamental building block for muscle tissue. Understanding the nuances of protein timing and muscle synthesis can be game-changing for those looking to maximize their gains.
This article delves into the importance of protein in bodybuilding, the concepts of protein timing and muscle synthesis, and offers insights into optimizing these elements for enhanced muscle growth.
Understanding Protein Timing and Muscle Synthesis
Protein timing refers to the strategic protein consumption around workouts to enhance muscle synthesis and recovery. It is significant because it can impact muscle repair and growth, optimizing the effects of resistance training.
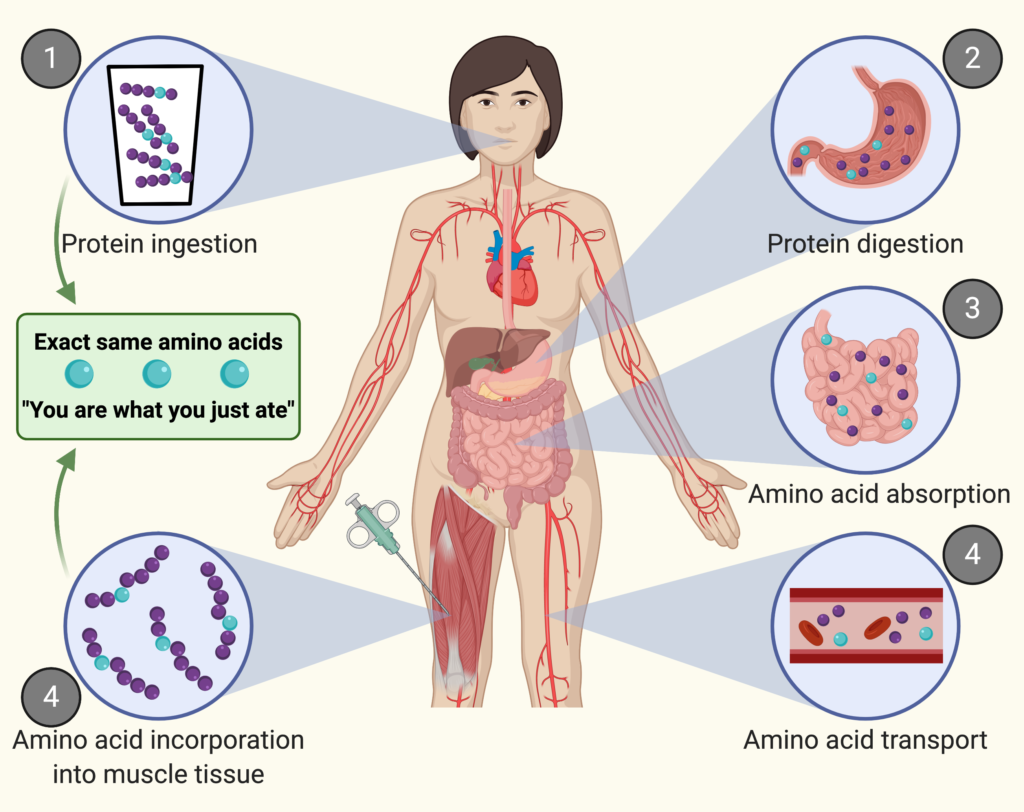
Muscle synthesis, or muscle protein synthesis (MPS), is the biological process in which the body builds new muscle proteins. Amino acids, the building blocks of protein, are critical for muscle synthesis. Leucine is a key player, stimulating muscle protein synthesis and promoting an anabolic response.

Anabolism is the metabolic state where the body builds muscle, while catabolism refers to the breakdown of muscle tissue. A balance between these two states is essential for effective muscle growth, emphasizing promoting an anabolic environment through adequate protein intake and timing.
The Science Behind Muscle Synthesis
Protein synthesis is a crucial biological process in which new proteins are created from amino acids. It plays a vital role in muscle repair and growth, enabling athletes to recover effectively from their workouts and ensuring that muscle fibers are adequately repaired and strengthened.
Muscle fibers are classified into two main types: slow-twitch and fast-twitch fibers, each serving a distinct function in muscle growth. Fast-twitch fibers are primarily responsible for hypertrophy—the increase in muscle size— and explosive strength, while slow-twitch fibers enhance endurance.
Hypertrophy occurs due to resistance training, wherein muscle fibers experience stress that leads to micro-tears. These micro-tears are subsequently repaired through protein synthesis, contributing to muscle growth.
Additionally, nutrients are utilized through various metabolic pathways that facilitate energy production and muscle repair. Understanding these pathways is essential for developing effective nutrition strategies that support muscle synthesis and overall athletic performance.
Optimal Protein Timing for Muscle Growth
The anabolic window is the optimal period after exercise when protein consumption can significantly enhance muscle recovery and growth. Consuming protein within this timeframe is critical for maximizing muscle protein synthesis.
Consuming protein before training can enhance performance and provide the body with amino acids during workouts, potentially improving muscle recovery and growth. Post-workout nutrition is essential for replenishing energy stores and repairing muscle. After training, consuming protein-rich foods or shakes provides the necessary amino acids for recovery.
Strategically planning protein intake throughout the day, rather than relying solely on pre-and post-workout nutrition, helps maintain a positive nitrogen balance and supports continuous muscle synthesis.
Practical Applications of Protein Timing
High-quality protein sources, such as whey and casein, are optimal for muscle synthesis. Whey protein is rapidly absorbed, making it an ideal choice for post-workout recovery, while casein provides a slow release of amino acids, making it suitable for overnight recovery.
Protein shakes serve as a convenient and effective way to meet protein requirements, particularly after exercise, as they can quickly deliver essential amino acids necessary for recovery.
Furthermore, utilizing a blend of different protein types can maximize muscle synthesis; combining fast-digesting proteins with slow-digesting ones ensures a steady supply of amino acids, enhancing overall muscle repair and growth.
Factors Influencing Protein Timing and Muscle Synthesis
Aligning protein intake with the training schedule is essential to ensure that the body receives the necessary nutrients for recovery and growth when they are most needed. Different exercise regimens can also impact protein requirements; for instance, resistance training often demands higher protein consumption due to the increased muscle breakdown and synthesis it entails.
Moreover, higher-intensity workouts generally require additional protein to support recovery effectively. Therefore, adjusting protein intake based on workout intensity can optimize muscle synthesis.
Finally, adequate rest periods play a critical role in muscle synthesis, allowing the body to repair and grow. It is essential to time protein intake strategically around these rest periods to maximize recovery and muscle development.
Nutritional Strategies for Enhancing Muscle Synthesis
A balanced diet is crucial for supporting muscle growth and overall health. It should include adequate amounts of protein, carbohydrates, and fats. Prioritizing nutrient-dense foods is essential in this dietary approach.
Nutrient partitioning plays a significant role in efficiently distributing these nutrients to enhance muscle synthesis while minimizing fat gain, thus optimizing the body’s use of available nutrients. Determining the right amount of protein intake for muscle growth; general recommendations suggest consuming between 1.6 to 2.2 grams per kilogram of body weight.
Additionally, balancing caloric intake is vital, as a caloric surplus is typically necessary for muscle growth, while a caloric deficit can lead to muscle loss. Understanding the role of macronutrients—proteins, fats, and carbohydrates—is vital for creating a diet that effectively supports muscle growth and aligns with overall fitness goals.
Scientific Research and Evidence
Numerous studies highlight the critical role of protein timing in optimizing muscle synthesis and recovery, demonstrating the significant benefits of strategic protein intake. Understanding how the body absorbs and utilizes protein is essential for selecting the most effective protein sources and timing, ensuring that consumed protein is used efficiently.
Additionally, the insulin response plays a vital role in nutrient uptake after workouts; a heightened insulin response facilitates the delivery of amino acids to muscle cells, promoting recovery and growth.
Maintaining a positive nitrogen balance is another important factor. It indicates effective muscle protein synthesis, making it a key metric for tracking progress in muscle growth.
Common Myths and Misconceptions
Common misconceptions about protein timing can hinder muscle growth. Addressing these myths with evidence can empower individuals to make informed decisions. Consulting healthcare providers for personalized dietary and nutritional advice is essential, especially for individuals with specific health concerns or goals.
Debunking popular fitness myths, particularly those regarding protein intake and timing, can help individuals focus on effective strategies for muscle growth.

Enhancing Overall Performance
Proper nutrition, particularly effective protein timing, is crucial in enhancing exercise performance, ultimately contributing to better workout outcomes. By implementing nutritional strategies that prioritize protein intake at the correct times, athletes can recover faster and promote improved muscle growth. Adequate protein consumption is essential for minimizing muscle breakdown, especially during intense training.
A comprehensive approach to sports nutrition encompasses understanding the significance of protein timing and synthesis, leading to enhanced athletic performance and quicker recovery for athletes.
Frequently Asked Questions
When is the best time to consume protein for optimal muscle growth?
The best times to consume protein are post-workout to aid recovery and throughout the day to ensure a consistent supply of amino acids.
Does training intensity affect protein requirements?
Higher-intensity workouts typically require more protein to support recovery and muscle synthesis.
How does nutrient partitioning impact muscle synthesis?
Nutrient partitioning involves effectively distributing nutrients to enhance muscle synthesis while minimizing fat gain.




