In bodybuilding, protein is essential for muscle growth and recovery. However, it’s not just about how much protein you consume—timing is crucial in maximizing gains. Protein timing involves strategically eating protein throughout the day to enhance muscle repair, promote hypertrophy, and improve workout performance.
The Science Behind Protein Timing
Protein timing is deeply rooted in how protein synthesis and muscle hypertrophy work. Protein synthesis is the body’s process of repairing muscle fibers damaged during intense training, building them stronger and larger. Amino acids, particularly leucine, are key drivers of this process, as they activate protein synthesis pathways crucial for muscle growth.
The “anabolic window” refers to the period immediately after a workout when muscle cells are most receptive to protein intake. During this window, muscles repair quickly, and timing your protein intake during this phase is essential for optimizing recovery and preventing muscle breakdown.
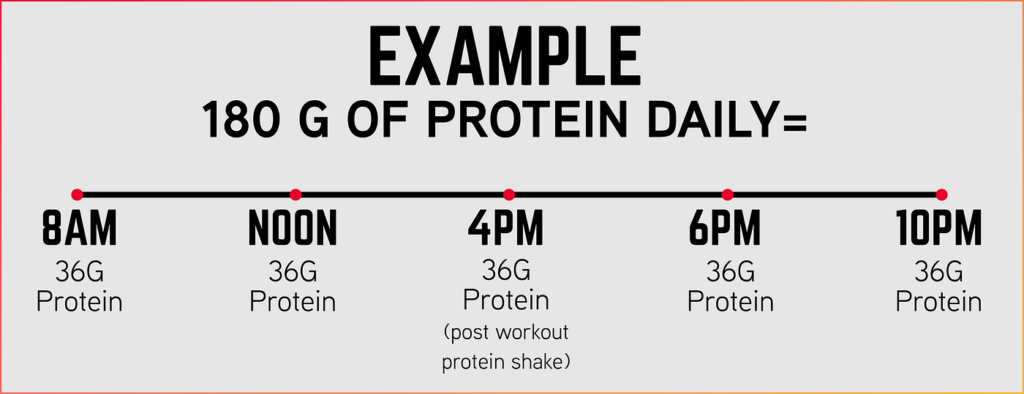
Key Times to Consume Protein
Pre-workout nutrition sets the stage for optimal performance. Eating protein before training helps maintain amino acid levels in the bloodstream, providing the muscles with the building blocks to prevent breakdown during intense exercise. Consuming protein before your workout ensures sustained energy and muscle protection, enabling you to push harder during training sessions.
Post-workout protein consumption is perhaps the most well-known aspect of protein timing. After a workout, muscles are in a state of repair, and protein is vital to kick-start recovery. Consuming protein within the anabolic window (30-60 minutes post-workout) accelerates recovery and prevents muscle breakdown, leading to better muscle gains.
Before bed, the body enters a prolonged fasting state, which can lead to muscle breakdown. Consuming slow-digesting proteins like casein before bed ensures a steady supply of amino acids throughout the night, maintaining an anabolic state and promoting muscle recovery while you sleep.
Optimizing Daily Protein Intake
Spreading your protein intake evenly throughout the day is critical for maintaining consistent muscle protein synthesis. Eating 20-40 grams of protein at regular intervals, such as during breakfast, lunch, dinner, and snacks, ensures that your muscles have a constant supply of amino acids to repair and grow.
When it comes to protein sources, not all are created equal. Whey protein is a fast-digesting protein ideal for post-workout recovery, while casein is slower-digesting and great for overnight repair.
BCAAs (branched-chain amino acids) are another popular option, especially during workouts. They are rapidly absorbed and can prevent muscle breakdown during training. Recovery drinks, often fortified with proteins and carbohydrates, can help replenish glycogen stores and provide amino acids for muscle repair post-workout.
Enhancing Protein Absorption and Utilization
Several factors affect how well your body digests and utilizes protein. Metabolism plays a role in how quickly protein is broken down and absorbed. Factors like the type of protein, meal composition, and individual metabolic rate can influence the rate of digestion. Insulin sensitivity also plays a role, as better insulin sensitivity helps shuttle amino acids into muscle cells more efficiently, promoting muscle repair and growth.
Carbohydrates are important for optimizing protein absorption. Consuming carbohydrates alongside protein post-workout helps spike insulin levels, which enhances amino acid uptake by muscle cells.
Similarly, staying hydrated supports muscle recovery and performance, as water helps transport nutrients throughout the body and aids in the digestion and absorption of protein.
Practical Tips for Implementing Protein Timing
Creating a structured meal plan is essential to making the most of protein timing. Calculate your daily protein needs based on your body weight and training intensity, and divide your intake across multiple meals.
Adhering to dietary guidelines emphasising balanced nutrition, including carbohydrates, fats, and protein, will help ensure a comprehensive approach to muscle growth.
Managing caloric intake is also crucial when planning your protein timing strategy. If your goal is to build muscle, you must maintain a caloric surplus, ensuring you consume more calories than you burn.
Balancing this surplus with the right protein intake will prevent muscle fatigue and ensure you’re not overloading your body with too many calories, which could lead to fat gain instead of muscle growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is protein timing important for muscle growth?
Timing your protein intake ensures that your muscles receive a steady supply of amino acids during key periods, such as after workouts or sleep. It helps maximize protein synthesis, repair muscle damage, and prevent muscle breakdown.
What type of protein is best before bed?
Casein protein, a slow-digesting protein, is ideal before bed because it provides a steady release of amino acids throughout the night, helping maintain an anabolic state while you sleep.
How often should I consume protein during the day?
It is recommended that protein be consumed every 3-4 hours throughout the day, spread evenly across meals and snacks, to keep muscle protein synthesis active and consistent.




